Elasticsearch是高度可伸缩的开源全文搜索和分析引擎。它允许我们快速实时地存储、搜索、分析大数据。
Elasticsearch使用Lucene作为内部引擎,但是在你使用它做全文搜索时,只需要使用统一开发好的API即可,而不需要了解其背后复杂的Lucene的运行原理。它的目的是通过简单的RESTful API来隐藏Lucene的复杂性,从而让全文搜索变得简单。
不过,Elasticsearch不仅仅是Lucene和全文搜索,我们还能这样去描述它:
- 分布式的实时文件存储,每个字段都被索引并可被搜索
- 分布式的实时分析搜索引擎
- 可以扩展到上百台服务器,处理PB级结构化或非结构化数据
关系型数据库和ES对比
| Relational DB | Elasticsearch |
|---|---|
| 数据库(database) | 索引(indices) |
| 表(tables) | types |
| 行(rows) | documents |
| 字段(columns) | fields |
数据管理(增删改查)
ES提供近乎实时的数据操纵和搜索能力。默认情况下,从索引/更新/删除数据到在搜索结果中出现数据之前,可以预期延迟一秒钟(刷新间隔)。这是与其他SQL数据库的重要区别,SQL数据库中的数据在事务完成后立即可用。
添加Document
接口: PUT /<index>/<type>/<ID>
现在我们往”customer”中创建一个ID为1 的document:
curl --location --request PUT 'localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1?pretty' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"name": "John Doe"
}'
运行结果如下:
{
"_index" : "customer",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1, //版本号,每修改一次+1
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1
}
通过上面的命令,我们已经成功的添加了一个customer document在customer index中。
值得注意的是,Elasticsearch不需要在显式地创建一个索引之前,我们就可以创建索引文档。在前面的示例中,如果没有事先已经存在索引,Elasticsearch将自动创建索引。
其中,ID为可选项,假如我们没有指定ID,ES则会自动生成一个唯一的ID,如下:
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "BDOQbn0B5XETjuLvc9yy", //自动生成唯一ID
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 2,
"_primary_term": 1
}
注意:我们这里使用了POST而不是PUT,如果使用PUT会提示错误:
{
"error": "Incorrect HTTP method for uri [/customer/_doc?pretty] and method [PUT], allowed: [POST]",
"status": 405
}
查询Document
接口:GET /<index>/<type>/<ID>
查询索引Customer中ID为1的Document命令:
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1?pretty"
查询结果如下:
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 2,
"_seq_no": 1,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "John Doe" //存储的内容
}
}
替换Document
接口:PUT /<index>/<type>/<ID>
添加Document时,假设ID已存在,如前面添加的ID为1,这将会覆盖原来的记录,如下:
curl --location --request PUT 'localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1?pretty' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"name": "zhang san"
}'
重新查询id=1,结果如下:
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 3, //版本号自增
"_seq_no": 3,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "zhang san"
}
}
注意“_version”已自增。
更新Document
接口:POST /<index>/<type>/<ID>/_update
更新customer中ID为1的Document中的name为“Tom”,并且添加新的字段age
curl --location --request POST 'localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1/_update?pretty' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"doc": { "name": "Tom", "age": 20 }
}'
查询结果如下:
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 4,
"_seq_no": 4,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "Tom",
"age": 20
}
}
如果我更新的时候参数只有部分字段或者不传已经有的字段,结果会怎样呢?
curl --location --request POST 'localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1/_update?pretty' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"doc": { "address": "安徽", "sex": "男" } //之前的name和age没有传
}'
查询结果如下:
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 5,
"_seq_no": 5,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "Tom", //还存在
"age": 20, //还存在
"address": "安徽",
"sex": "男"
}
}
看来_update接口会 保留已存在的字段,不会直接覆盖,这是和替换接口最大的区别。
删除Document
接口:DELETE /<index>/<type>/<ID>
删除customer中ID为2的Document
curl --location --request DELETE 'localhost:9200/customer/_doc/2?pretty'
假设文档不存在,则返回如下:
{
"_index" : "customer",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "not_found", //文档不存在
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1
}
我们先添加一条数据,然后再删除,删除结果如下:
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 3,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 8,
"_primary_term": 1
}
再次查询id=2,数据不存在,结果如下:
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "2",
"found": false
}
批量处理(demo)
接口:POST <index>/<type>/_bulk
在ES中,除了上面针对单个Document增、删、改、查之外,ES还提供了一个强大的API_bulk,它具备了批量操作的能力。
批量添加
批量添加2个Document
curl -X POST "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/_bulk?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{"index":{"_id":"11"}}
{"name": "Milton" }
{"index":{"_id":"22"}}
{"name": "Cherish" }
'
结果如下:
{
"took" : 272,
"errors" : false,
"items" : [
{
"index" : {
"_index" : "customer",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "11",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 3,
"status" : 201
}
},
{
"index" : {
"_index" : "customer",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "22",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 3,
"status" : 201
}
}
]
}
通过上面可知,已经新增的两条Document。
批量更新和删除
curl -X POST "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/_bulk?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{"update":{"_id":"11"}} //更新
{"doc": { "name": "Milton Love Cherish" } }
{"delete":{"_id":"22"}} //删除
'
运行结果如下:
{
"took" : 269,
"errors" : false,
"items" : [
{
"update" : {
"_index" : "customer",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "11",
"_version" : 2,
"result" : "updated",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 3,
"status" : 200
}
},
{
"delete" : {
"_index" : "customer",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "22",
"_version" : 2,
"result" : "deleted",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 2,
"_primary_term" : 3,
"status" : 200
}
}
]
}
批量创建/更新 index
POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "teacher", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "1" } }
{ "name" : "Milton" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "teacher", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2" } }
{ "name" : "Cherish" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "teacher", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "3" } }
{ "name" : "Evan" }
批量创建 create
POST _bulk
{ "create" : { "_index" : "teacher", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "4" } }
{ "name" : "yangp" }
{ "create" : { "_index" : "teacher", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "5" } }
{ "name" : "yangf" }
index 和 create 都可以增加文档。使用index时,如果记录已存在,则会进行更新,如果不存在,则会新增;但是使用create时,如果记录已存在,则会创建失败。
批量更新 update
POST /teacher/_doc/_bulk
{ "update" : { "_id" : "4" } }
{"doc":{ "name" : "yangp_update" }}
{ "update" : { "_id" : "5" } }
{"doc":{ "name" : "yangf_update" }}
批量删除 delete
POST /teacher/_doc/_bulk
{"delete":{"_id":"4"}}
{"delete":{"_id":"5"}}
批量获取 _mget
获取索引teacher中,id为1,2的document
GET /teacher/_doc/_mget
{
"ids":["1","2"]
}
GET /teacher/_mget
{
"docs":[
{
"_type":"_doc",
"_id":"1"
},
{
"_type":"_doc",
"_id":"2"
}
]
}
查询方式有多种,这里只展示2种。
匹配删除_delete_by_query
从索引teacher中删除name为“Evan”的document
POST /teacher/_delete_by_query
{
"query":{
"match": {
"name": "Evan"
}
}
}
匹配更新_update_by_query
从索引teacher中,更新name包含“Milton”的文档,设置其gener=“Boy”,age=100
POST /teacher/_update_by_query
{
"query":{
"match": {
"name": "Milton"
}
},
"script":{
"source":"ctx._source.gener=params.gener;ctx._source.age=params.age",
"params":{
"gener":"Boy"
,
"age":100
}
}
}
搜索API _search
测试数据准备
在开始探索之前,我们先下载官方提供的样例数据集,导入到我们的集群中。
百度云盘链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/15wtt3olKf06KxugXSqMq2w 提取码: vse4
将下载的accounts.json 上传到当前ES服务器目录中,执行以下命令
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPOST "localhost:9200/bank/_doc/_bulk?pretty&refresh" --data-binary "@accounts.json"
首先,我们查询es的所有索引
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v"
结果出现了很多索引,因为之前安装了elk等其他工具,直接忽略其他索引,重点关注本次导入的索引bank。
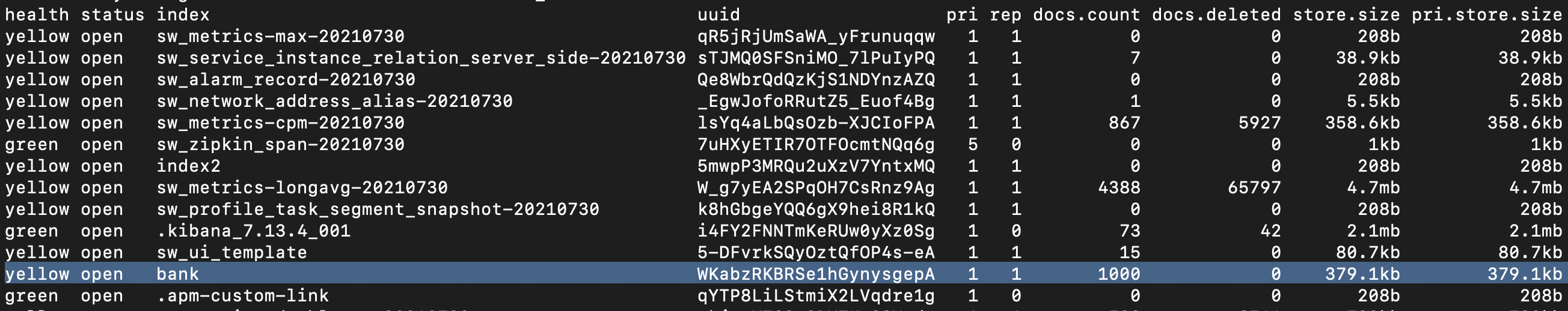
发现已经新增了索引bank,其中有1000个document。
我们有两种方式进行搜索:
- 在请求URL中传参
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/bank/_search?q=*&sort=account_number:asc&pretty"
- 在请求BODY中传参
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"sort": [
{ "account_number": "asc" }
]
}
通常,我们会选择在BODY中使用JSON格式进行传参。
上面两种方式,查询的结果是一样的。查询关键字为*,代表所有值。
排序是根据account_number升序,默认是返回10条数据。返回格式如下:
{
"took" : 19, //查询时间
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 100, //匹配的document数量
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ //匹配的document,多个
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "9",
"_score" : null,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 9,
"balance" : 24776,
"firstname" : "Opal",
"lastname" : "Meadows",
"age" : 39,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "963 Neptune Avenue",
"employer" : "Cedward",
"email" : "opalmeadows@cedward.com",
"city" : "Olney",
"state" : "OH"
},
"sort" : [
9
]
}
......
]
}
}
查询语句
基本参数选项:query、from、size、sort、_source
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {"match_all": {}},
"from": 10,
"size": 2,
"sort": [
{"balance": { "order": "desc" } }
],
"_source":["account_number","balance"]
}
query:指定查询条件,这里使用{ "match_all": {} }表示查询条件匹配所有记录 from:表示从第n条匹配记录开始取值,默认为0 size:表示匹配条数,默认10 sort:表示排序,这里使用{ "balance": { "order": "desc" }},表示按balance降序排序,这里也可以写成[{ "balance": "desc" }] _source:表示查询字段,这里使用["account_number", "balance"]表示返回结果中,只需要返回”account_number”, “balance”两个字段即可。默认返回所有字段。 上面的查询结果如下:
{
"took": 34,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1000, //查询总数
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": null,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bank",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "255",
"_score": null,
"_source": { //结果只有以下2个字段
"account_number": 255,
"balance": 49339
},
"sort": [
49339
]
},
{
"_index": "bank",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "524",
"_score": null,
"_source": {
"account_number": 524,
"balance": 49334
},
"sort": [
49334
]
}
]
}
}
查询匹配条件
上面例子中,我们在选项query中,使用了{ "match_all": {} }表示查询条件匹配所有记录,下面以一系列的例子介绍各种匹配条件
match查询
查询 account_number=20 的document
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {"account_number": 20}
}
}
查询结果如下:
{
"took": 6,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bank",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "20",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"account_number": 20, //match字段
"balance": 16418,
"firstname": "Elinor",
"lastname": "Ratliff",
"age": 36,
"gender": "M",
"address": "282 Kings Place",
"employer": "Scentric",
"email": "elinorratliff@scentric.com",
"city": "Ribera",
"state": "WA"
}
}
]
}
}
查询 address 中包含 “mill” 的document
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {"address": "mill"}
}
}
查询 address 中包含 “mill” 或者 “lane” 的document
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {"address": "mill lan"}
}
}
match_phrase短语查询
查询 address 中包含短语 “mill lane” 的document
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {"address": "mill lane"}
}
}
bool and关系查询
查询 address 中同时包含 “mill” 和 “lane” 的document
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "address": "mill" } },
{ "match": { "address": "lane" } }
]
}
}
}
bool or 关系查询
查询 address 中包含 “mill” 或者 “lane” 的document
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{ "match": { "address": "mill" } },
{ "match": { "address": "lane" } }
]
}
}
}
bool not关系查询
查询 address 中即不存在 “mill” 也不存在 “lane” 的document
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{ "match": { "address": "mill" } },
{ "match": { "address": "lane" } }
]
}
}
}
bool 组合查询
查询 age=40,state!=”ID” 的document
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "age": 40 } }
],
"must_not": [
{ "match": { "state": "ID" } }
]
}
}
}
bool filter查询
查询 20000<=balance<=30000 的document
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter":{
"range": {
"balance": {
"gte": 20000,
"lte": 30000
}
}
}
}
}
}
结语
暂时API分享这么多,后续会补充。
文档信息
- 本文作者:yindongxu
- 本文链接:https://iceblow.github.io/2021/11/26/Elasticsearch/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)