MyBatis的底层操作封装了JDBC的API,MyBatis的核心对象(SqlSession,Executor)与JDBC的核心对象(Connection,Statement)相互对应。
本文的核心观点是:从JDBC入手并立足于JDBC,才能深入的理解MyBatis的工作原理以及核心流程。
概念
JDBC有四个核心对象:
- DriverManager,用于注册数据库连接
- Connection,与数据库连接对象
- Statement/PrepareStatement,操作数据库SQL语句的对象
- ResultSet,结果集或一张虚拟表
MyBatis也有四大核心对象:
- SqlSession对象,该对象中包含了执行SQL语句的所有方法【1】。类似于JDBC里面的Connection 【2】。
- Executor接口,它将根据SqlSession传递的参数动态地生成需要执行的SQL语句,同时负责查询缓存的维护。类似于JDBC里面的Statement/PrepareStatement。
- MappedStatement对象,该对象是对映射SQL的封装,用于存储要映射的SQL语句的id、参数等信息。
- ResultHandler对象,用于对返回的结果进行处理,最终得到自己想要的数据格式或类型。可以自定义返回类型。
工作原理
MyBatis的工作原理如下图所示:
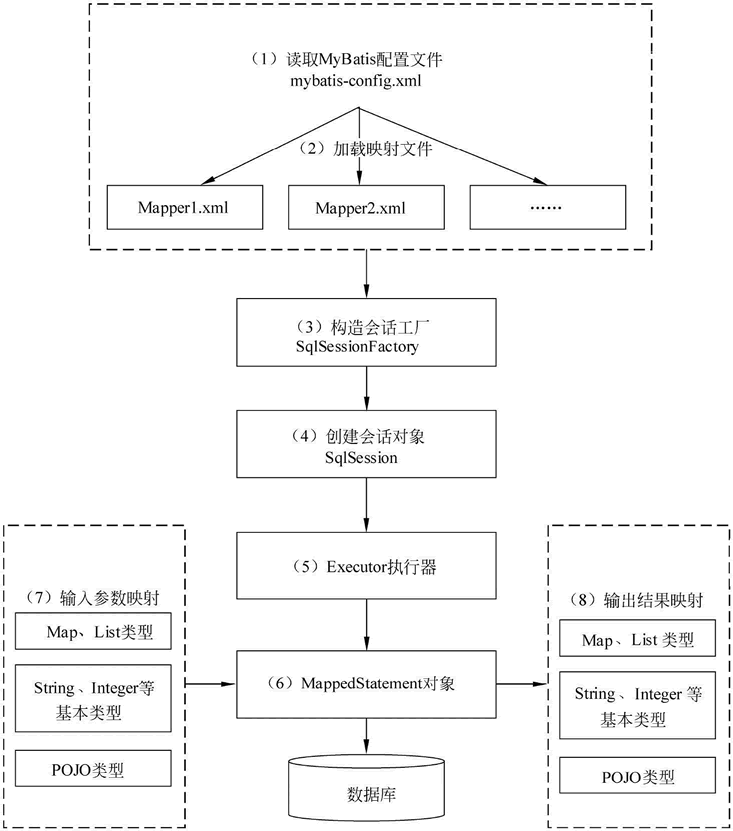
(1)读取MyBatis的配置文件。mybatis-config.xml为MyBatis的全局配置文件,用于配置数据库连接信息。
(2)加载映射文件。映射文件即SQL映射文件,该文件中配置了操作数据库的SQL语句,需要在MyBatis配置文件mybatis-config.xml中加载。mybatis-config.xml 文件可以加载多个映射文件,每个文件对应数据库中的一张表。
(3)构造会话工厂。通过MyBatis的环境配置信息构建会话工厂SqlSessionFactory。
(4)创建会话对象。由会话工厂创建SqlSession对象,该对象中包含了执行SQL语句的所有方法。
(5)Executor执行器。MyBatis底层定义了一个Executor接口来操作数据库,它将根据SqlSession传递的参数动态地生成需要执行的SQL语句,同时负责查询缓存的维护。
(6)MappedStatement对象。在Executor接口的执行方法中有一个MappedStatement类型的参数,该参数是对映射信息的封装,用于存储要映射的SQL语句的id、参数等信息。
(7)输入参数映射。输入参数类型可以是Map、List等集合类型,也可以是基本数据类型和POJO类型。输入参数映射过程类似于JDBC对preparedStatement对象设置参数的过程。
(8)输出结果映射。输出结果类型可以是Map、List等集合类型,也可以是基本数据类型和POJO类型。输出结果映射过程类似于JDBC对结果集的解析过程。
源码分析
SqlSessionFactory
每个基于 MyBatis 的应用都是以一个 SqlSessionFactory 的实例为核心的。
SqlSessionFactory 的实例可以通过 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 获得。
而 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 则可以从 XML 配置文件或一个预先配置的 Configuration 实例来构建出 SqlSessionFactory 实例。
XML构建
String resource = "./mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
核心配置包括数据源、事务管理器,也包含了Mapper映射器。
xml文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/example/BlogMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
代码构建
DataSource dataSource = BlogDataSourceFactory.getBlogDataSource();
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = new JdbcTransactionFactory();
Environment environment = new Environment("development", transactionFactory, dataSource);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(environment);
configuration.addMapper(BlogMapper.class);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(configuration);
源码
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
// 获取SqlSession实例
SqlSession openSession();
SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(Connection connection);
SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection);
Configuration getConfiguration();
}
SqlSession
SqlSession 提供了在数据库执行 SQL 命令所需的所有方法,我们可以从SqlSessionFactory获取SqlSession实例。
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
Blog blog = (Blog) session.selectOne("org.mybatis.example.BlogMapper.selectBlog", 101);
}
源码
public interface SqlSession extends Closeable {
// 所有查询语句
<E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter);
<K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String statement, Object parameter, String mapKey);
void select(String statement, Object parameter, ResultHandler handler);
int update(String statement, Object parameter);
void commit();
void rollback();
......
}
MappedStatement
该对象是对映射SQL的封装,用于存储要映射的SQL语句的id、参数等信息。
所有的MappedStatement 都是存储在 Configuration类
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection")
.conflictMessageProducer((savedValue, targetValue) ->
". please check " + savedValue.getResource() + " and " + targetValue.getResource());
SqlSession的实现类会获取 MappedStatement,然后调用Executor类的接口执行,以实现类DefaultSqlSession查询接口为例:
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
Executor
它将根据SqlSession传递的参数动态地生成需要执行的SQL语句,同时负责查询缓存的维护。
源码
Executor接口提供多个方法,包括增删改查、事务提交回滚、查询缓存等。
public interface Executor {
ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null;
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException;
List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException;
void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException;
void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException;
CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql);
boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key);
void clearLocalCache();
void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType);
Transaction getTransaction();
void close(boolean forceRollback);
boolean isClosed();
void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor);
}
实现类BatchExecutor
BatchExecutor是 Executor的其中一个实现类,查询方法逻辑如下:
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
flushStatements();
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
Connection connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog());
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
ResultHandler
用于对返回的结果进行处理,最终得到自己想要的数据格式或类型。
源码
public interface ResultHandler<T> {
void handleResult(ResultContext<? extends T> resultContext);
}
总结
要了解mybatis的工作原理,重点要掌握4个核心对象以及它们的流程图。
文档信息
- 本文作者:yindongxu
- 本文链接:https://iceblow.github.io/2022/03/29/Mybatis%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)